MIoU 定义
Mean Intersection over Union(MIoU,均交并比)为语义分割的标准度量。其计算两个集合的交集和并集之比,在语义分割问题中,这两个集合为真实值(ground truth)和预测值(predicted segmentation)。这个比例可以变形为 TP(交集)比上 TP、FP、FN 之和(并集)。在每个类上计算 IoU,然后取平均。
MIoU=1k+1k∑i=0pii∑kj=0pij+∑kj=0pji−piipij 表示真实值为 i,被预测为 j 的数量。
直观理解
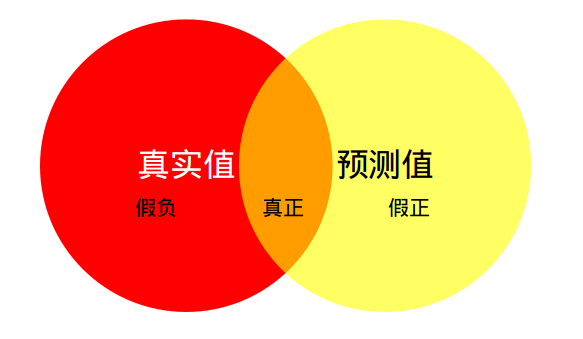
红色圆代表真实值,黄色圆代表预测值。橙色部分为两圆交集部分。
- MPA(Mean Pixel Accuracy,均像素精度):计算橙色与红色圆的比例;
- MIoU:计算两圆交集(橙色部分)与两圆并集(红色+橙色+黄色)之间的比例,理想情况下两圆重合,比例为 1。
TensorFlow源码解析
TensorFlow 主要用 tf.metrics.mean_iou 来计算 MIoU,下面解析源码:
第一步:计算混淆矩阵
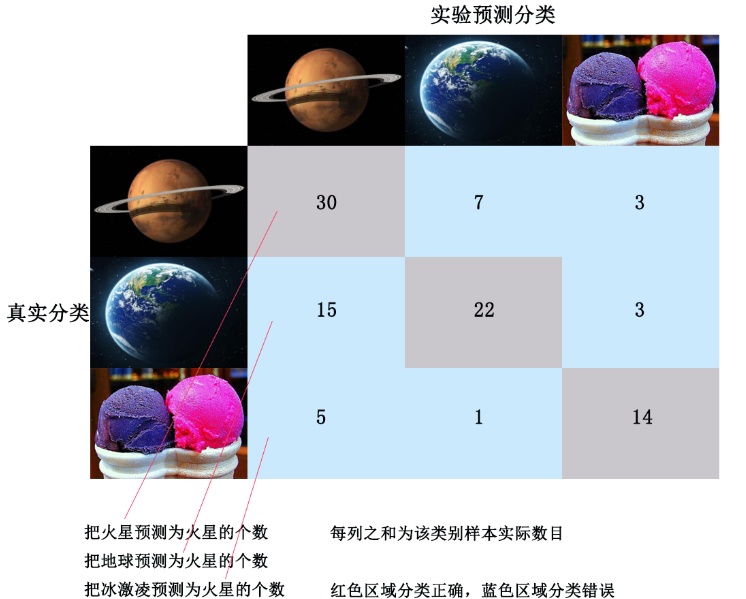
混淆矩阵例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 主要代码
def confusion_matrix(labels, predictions, num_classes=None, dtype=dtypes.int32,
name=None, weights=None):
# 例子:labels = [0, 1, 2, 0, 3]
# predictions =[0, 1, 1, 3, 3]
if num_classes is None: # 不指定类别个数,就以 labels 或者 predictions 最大的指定,即4
num_classes = math_ops.maximum(math_ops.reduce_max(predictions),
math_ops.reduce_max(labels)) + 1
else:
num_classes_int64 = math_ops.cast(num_classes, dtypes.int64)
labels = control_flow_ops.with_dependencies(
[check_ops.assert_less(
labels, num_classes_int64, message='`labels` out of bound')],
labels)
predictions = control_flow_ops.with_dependencies(
[check_ops.assert_less(
predictions, num_classes_int64,
message='`predictions` out of bound')],
predictions)
if weights is not None:
predictions.get_shape().assert_is_compatible_with(weights.get_shape())
weights = math_ops.cast(weights, dtype)
shape = array_ops.stack([num_classes, num_classes])
indices = array_ops.stack([labels, predictions], axis=1)
# indices = [[0,0],[1,1],[2,1],[0,3],[3,3]]
values = (array_ops.ones_like(predictions, dtype)
if weights is None else weights)
# 对应位置的 values,若不指定,则全为 1
cm_sparse = sparse_tensor.SparseTensor(
indices=indices, values=values, dense_shape=math_ops.to_int64(shape))
# 稀疏张量,指定 indices 位置为指定 value,其他位置为 0
# 多次指定一个位置,value 为多次相加的结果
zero_matrix = array_ops.zeros(math_ops.to_int32(shape), dtype)
return sparse_ops.sparse_add(zero_matrix, cm_sparse)
SparseTensor 例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.SparseTensor(indices=[[0,0], [1,2], [0, 0]], values=[1, 1, 1], dense_shape=[3, 4])
zero_m = array_ops.zeros(math_ops.to_int32([3,4]),dtype=tf.int32)
r = sparse_ops.sparse_add(zero_m, a)
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(device_count={'cpu':0}))
sess.run(r)
# array([[2, 0, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 1, 0],
# [0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)
第二步:计算 MIoU
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
def compute_mean_iou(total_cm, name):
"""Compute the mean intersection-over-union via the confusion matrix."""
sum_over_row = math_ops.to_float(math_ops.reduce_sum(total_cm, 0))
sum_over_col = math_ops.to_float(math_ops.reduce_sum(total_cm, 1))
cm_diag = math_ops.to_float(array_ops.diag_part(total_cm)) # 交集
denominator = sum_over_row + sum_over_col - cm_diag # 分母,即并集
# The mean is only computed over classes that appear in the
# label or prediction tensor. If the denominator is 0, we need to
# ignore the class.
num_valid_entries = math_ops.reduce_sum(
math_ops.cast(
math_ops.not_equal(denominator, 0), dtype=dtypes.float32)) # 类别个数
# If the value of the denominator is 0, set it to 1 to avoid
# zero division.
denominator = array_ops.where(
math_ops.greater(denominator, 0), denominator,
array_ops.ones_like(denominator))
iou = math_ops.div(cm_diag, denominator) # 各类IoU
# If the number of valid entries is 0 (no classes) we return 0.
result = array_ops.where(
math_ops.greater(num_valid_entries, 0),
math_ops.reduce_sum(iou, name=name) / num_valid_entries, 0) #mIoU
return result
通过 tf.metrics.mean_iou 的API可以得到 MIoU,但并没有把各类 IoU 释放出来,为了计算各类 IoU,可以修改上面的代码,获取 IoU 中间结果,也可以用 weight 的方式变相计算。
基本思路就是把只保留一类的 IoU,其他类 IoU 置零,然后最后将 MIoU * num_classes 就可以了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
tp_position = tf.equal(tf.to_int32(labels), tf.to_int32(predictions))
label_0_weight = tf.where((tp_position & tf.not_equal(labels, 0)), tf.zeros_like(labels),
tf.ones_like(labels))
## 混淆矩阵对角线上只保留一类非 0,其他类都置 0
metric_map['IOU/class_0_iou'] = tf.metrics.mean_iou(
predictions, labels, dataset.num_classes, weights=label_0_weight)
## 结果是 0 类 IoU / num_classes
PyTorch 源码解析
PyTorch 基本计算思路和上面是一样的,代码很简洁,就不过多介绍了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
class IOUMetric:
"""
Class to calculate mean-iou using fast_hist method
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.hist = np.zeros((num_classes, num_classes))
def _fast_hist(self, label_pred, label_true):
mask = (label_true >= 0) & (label_true < self.num_classes)
hist = np.bincount(
self.num_classes * label_true[mask].astype(int) +
label_pred[mask], minlength=self.num_classes ** 2).reshape(self.num_classes, self.num_classes)
return hist
def add_batch(self, predictions, gts):
for lp, lt in zip(predictions, gts):
self.hist += self._fast_hist(lp.flatten(), lt.flatten())
def evaluate(self):
acc = np.diag(self.hist).sum() / self.hist.sum()
acc_cls = np.diag(self.hist) / self.hist.sum(axis=1)
acc_cls = np.nanmean(acc_cls)
iu = np.diag(self.hist) / (self.hist.sum(axis=1) + self.hist.sum(axis=0) - np.diag(self.hist))
mean_iu = np.nanmean(iu)
freq = self.hist.sum(axis=1) / self.hist.sum()
fwavacc = (freq[freq > 0] * iu[freq > 0]).sum()
return acc, acc_cls, iu, mean_iu, fwavacc